Vertical Shaft
Construction at the Pump Storage Plant
Vianden/Luxembourg
The capacity of the pump storage plant Vianden in Luxembourg is to be increased. Part of the structures to be built is a vertical pressure shaft that was drilled using a newly developed Raise Boring Rig by Herrenknecht and Edilmac dei F.lli Maccabelli S.r.l.
1 New capacities for the pump storage plant Vianden
The pump storage plant (PSP) Vianden/Luxembourg was put into operation in 1963/1964 with 9 sets of machines and in the mid-1970s it was extended to include a 10th machine unit. Pump storage plants are primarily used for peak load protection. Water flows from an elevated basin (upper reservoir) through pump turbines into a lower-lying basin (lower reservoir) and thus generates electricity. When necessary, for example, when there is a surplus on the electricity market, the water is pumped from the lower to the upper reservoir. The PSP Vianden has a capacity of 1,100 MW with its 10 machine units. The operator, Société Électrique de l‘Our (SEO), extends the capacity by 200 MW through the installation of an 11th machine unit, which uses the existing upper and lower basins, but has its own system of waterways and inlet and outlet stuctures.
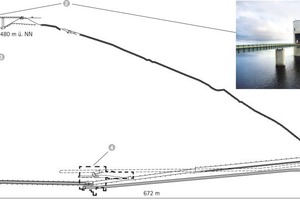
The construction of the facilities to accommodate the 11thmachine, was under the responsibility of the consortium PSW Vianden Los 1, consisting of the companies Züblin, Strabag and Jäger. The contract included, among others, the construction of an inlet and outlet tower in the upper reservoir, followed by a vertical pressure shaft (Figure 1).
2 The construction of the pressure shaft
The contract for the construction of the pressure shaft was awarded to Edilmac dei F.lli Maccabelli S.r.l. by the consortium Vianden. The pressure shaft extends to 300 m from the upper reservoir down to the powerhouse level. After passing through a vertical bend, a 240 m long, shallow inclined pressure tunnel connects to the power house. The vertical shaft, manifold and pressure tunnels are equipped with a steel armor, which is designed to accommodate the full, potential outside water pressure. The pressure shaft and tunnel will have an internal diameter of 4.50 m.
The project area is located in the clayey to silty fine sand of the Siegen and Ems steeps of the Lower Devonian, whereby generally very low to impermeable ground water conditions was assumed. According to the tender documents, the raise boring method was selected for the construction of the vertical pressure shaft.
3 Applications of the Raise Boring Rig
After the contract was awarded in April 2010, Herrenknecht developed the Raise Boring Rig 550 VF (Figure 2). Here, customer-specific requirements were incorporated. The successful factory acceptance test took place on October 5, 2010. Favored by the compact, modular design, the rig could be delivered from the factory in Schwanau to the Vianden site with only a few transports where it arrived on October 8, 2010.
3.1 Description of the raise boring procedure
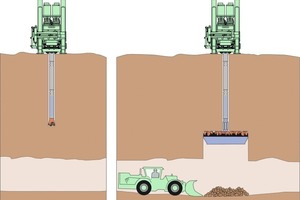
When using a Raise Boring Rig for a shaft construction in stable rock, the handling of the rig, over the shaft starting point, takes place in a first step by means of a crawler track or crane. From here the vertical pilot hole starts with the drill bit facing downwards (Figure 3a). If necessary, the pilot hole can be carried out at an angle of up to 45°. The debris is flushed out during the pilot hole by a flushing medium (e.g. water, air). Depending on the drilling depth, additional drill rods are successively installed until the target depth is reached in the existing lower tunnel or cavern. The pilot hole drill bit is then removed and the reaming head (typically 1 to 7 m in diameter) mounted on the drill string. The rig pulls up the reaming head with the drill string (Figure 3b). Through the rotation of the reaming head, the rock is crushed and falls down where it is removed. The shaft is reamed from the bottom to the top by the diameter of the reaming head to the target dimension.
Compared with the conventional shaft sinking methods, the use of a raise boring method significantly increases the safety of the personnel, since they work outside the actual shaft. In addition, significantly higher construction rates can be achieved. The shaft wall is generally smoother with a simultaneously reduced over-excavation. Dropping of the muck on a lower level is associated with less effort. Since fewer staff is needed to operate the rig than with conventional shaft sinking, significant cost savings can be achieved here.
3.2 Execution of the drilling in Vianden
During on-site assembly, the construction team had to mount the Raise Boring Rig 550 VF in a 45 m high inlet/outlet tower under significantly confined space. Nevertheless, the on-site assembly was completed in 3 days. On November 16, 2010, the rig was put into operation as planned and the pilot hole (diameter 15“/381 mm) was drilled. In the course of the reaming (5,460 mm diameter), 10 m/day were achieved on the average (max. 18 m/day).
With the constantly changing geological conditions of loose to hard rock with maximum compressive strengths of up to 130 MPa, the machine control system proved to be particularly favorable, ensuring a failure-free boring process. The time schedule for assembly, pilot boring, reaming and disassembly was met after 40 drilling days. On January 18, 2011 the drilling of the 282-m long shaft was completed (Figure 4a and b).
3.3 Characteristics of the Raise Boring Rig 550 VF
The RBR 550 VF is one of the largest rigs of its kind ever used. It is distinguished by a compact, modular design and has a powerful and highly efficient center-free drive. Herrenknecht‘s proven variable frequency controlled drive concept allows for variable speed and torque control. The rig is designed for shaft lengths of up to 1,000 m. The mechanized drill pipe handling ensures more efficient operations as well as greater safety of personnel during installation and removal of drilling rods.
4 Summary and outlook
The Raise Boring Rig 550 VF has already proven itself in its premiere in Vianden with high reliability. The pressure shaft for the 11th machine unit of the Vianden pump storage plant was quickly and safely excavated. The commissioning of the 11th machine unit is scheduled for the third quarter of 2013. After its use in Luxembourg the next task for the Raise Boring Rig 550 VF is at hand: a shaft (4,760 mm diameter and 280 m depth) for the ventilation of the tunnel bypass in Bolzano/Italy. At the construction site in Bolzano the crawler unit of the RBR 550 VF proved its worth, in that the location with its difficult access conditions could be easily reached.
The mechanical excavation of shafts using the raise boring method is ideal for a variety of applications: Ventilation shafts, ore and waste passes, hoisting shafts, supply shafts (energy, water and air) and pressure shafts for hydroelectric power plants, as in the case described above.